Dodge Charger Throttle Body Problems: Diagnosis and Fixes

Common Dodge Charger throttle body problems include: issues with the throttle position sensor, a failing throttle actuator motor, carbon buildup causing the throttle plate to stick, and potential electrical connection problems which can lead to symptoms like rough idling, hesitation during acceleration, decreased engine power, and check engine lights due to related diagnostic codes.
Common Symptoms of Throttle Body Problems
Electronic Throttle Control (ETC) Light
The ETC light is a key indicator of throttle body issues. If the light blinks, it usually points to minor inconsistencies in the throttle system, which might resolve temporarily with a reset. However, if the light stays solid, it signifies a more serious issue such as a failing throttle position sensor or a mechanical fault in the throttle body assembly. This light often triggers “limp mode,” where the vehicle restricts RPM to prevent further damage. This safety feature, while protective, significantly reduces drivability.
Engine Shut-Off
Many owners report sudden engine shut-offs, especially during high-speed driving or heavy acceleration. This occurs when the throttle system fails to communicate effectively with the engine control module (ECM), leading to a complete shutdown as a protective measure. Engine shut-offs are not only inconvenient but also potentially hazardous if they occur in traffic
Overheating and ETC Light Together
When overheating occurs alongside the ETC light, it usually indicates a secondary issue impacting the throttle system, such as a failing water pump, low coolant levels, or a stuck thermostat. Overheating can cause the throttle body to malfunction by interfering with electrical components or causing thermal stress on the sensor connections. Resolving the overheating issue is essential to restoring throttle body functio
Car Won’t Start
When the throttle body fails entirely, the car may refuse to start. This happens because the throttle plate cannot open to allow airflow into the engine for combustion. In some cases, a complete failure of the electronic throttle control system will immobilize the vehicle until repairs are made.
Also Read: Ram 1500 Traction Control Light On (Why
Diagnosing Throttle Body Issues
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS):
The TPS monitors the angle of the throttle plate and communicates this data to the engine control module. When the TPS fails, it sends incorrect signals, causing erratic engine behavior such as RPM surges, reduced power, or limp mode. A malfunctioning sensor can also cause excessive fuel consumption, as the engine cannot accurately adjust the air-fuel mixture.
Wiring Problems:
Damaged or loose wiring to the throttle body can cause intermittent faults or a complete loss of function. Vibrations, engine heat, and age can deteriorate wiring insulation, leading to short circuits or open connections. Inspecting the wiring harness for visible damage and testing for continuity can identify and resolve these issues.
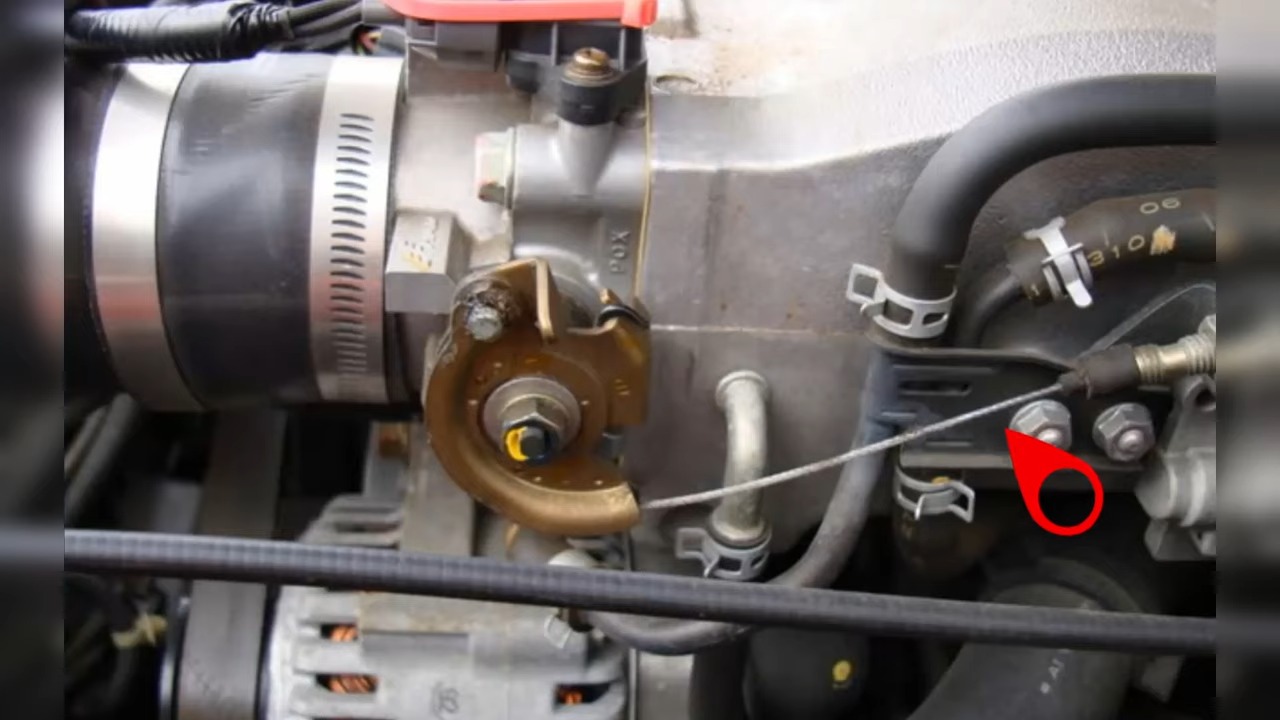
Dirty Throttle Body:
A dirty throttle body is one of the most common and easiest-to-fix problems. Dust, oil residue, and carbon buildup can block the throttle plate, causing it to stick or fail to open fully. This limits the airflow into the engine, leading to poor performance and inconsistent idling. Regular cleaning with throttle body cleaner can prevent these problems from occurring.
PCM or Software Issues:
Custom tunes or outdated engine software can interfere with throttle body performance. The powertrain control module (PCM) relies on precise programming to manage throttle inputs, and any mismatch or corruption in the software can lead to unexpected behavior. Reflashing the PCM with updated software often resolves these compatibility issues.
Steps to Address Throttle Body Issues
- Check for Codes
Using an OBD-II scanner, read the diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) stored in the system. Codes like P2101 (throttle actuator control motor circuit) or P2110 (limp mode activation) provide a starting point for troubleshooting. Clearing the codes after repairs ensures the problem has been resolved and helps prevent the issue from recurring. - Inspect and Clean the Throttle Body
Remove the air intake and visually inspect the throttle body. Look for signs of carbon buildup, dirt, or debris obstructing the throttle plate. Use a throttle body cleaner and a soft brush to remove these deposits. Be gentle to avoid damaging the throttle plate or sensors. - Reset the ETC
Disconnect the battery for at least 30 minutes to reset the electronic throttle control system. After reconnecting, perform a throttle relearn by turning the ignition to the “run” position (without starting the engine), pressing the accelerator pedal slowly to the floor, and releasing it three times. This helps the PCM recalibrate the throttle plate position. - Test Wiring and Connections
Check the throttle body wiring harness for visible damage, such as frayed wires or corroded terminals. Test the continuity of the wires using a multimeter. Repair any damaged wires or replace the harness if necessary. - Replace Components if Necessary
If cleaning and resets fail, the throttle body itself may need replacement. Upgrading to a ported throttle body can improve airflow and engine performance, particularly for high-performance models like the R/T. Ensure the new throttle body is compatible with your Charger model.